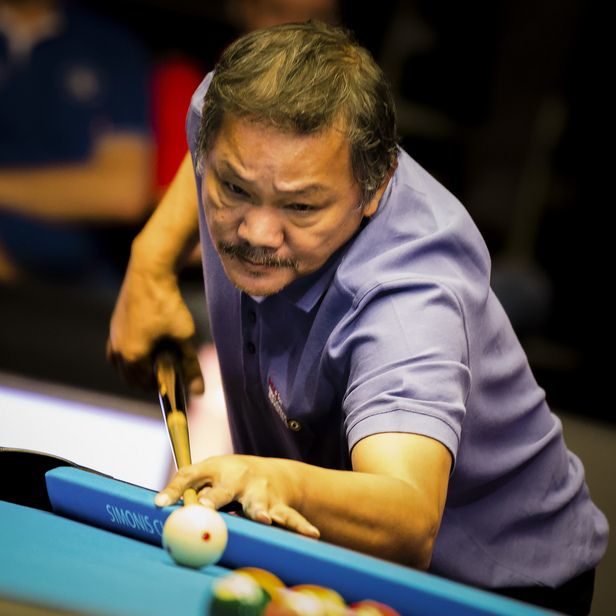
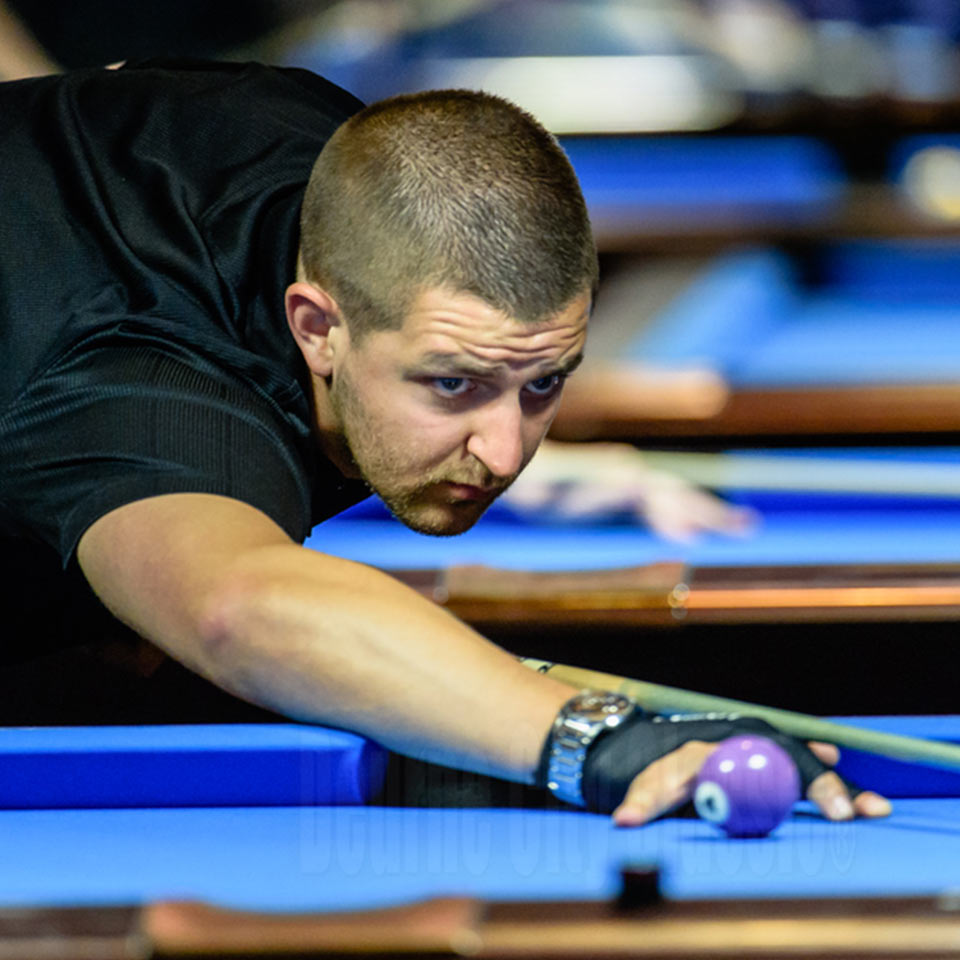
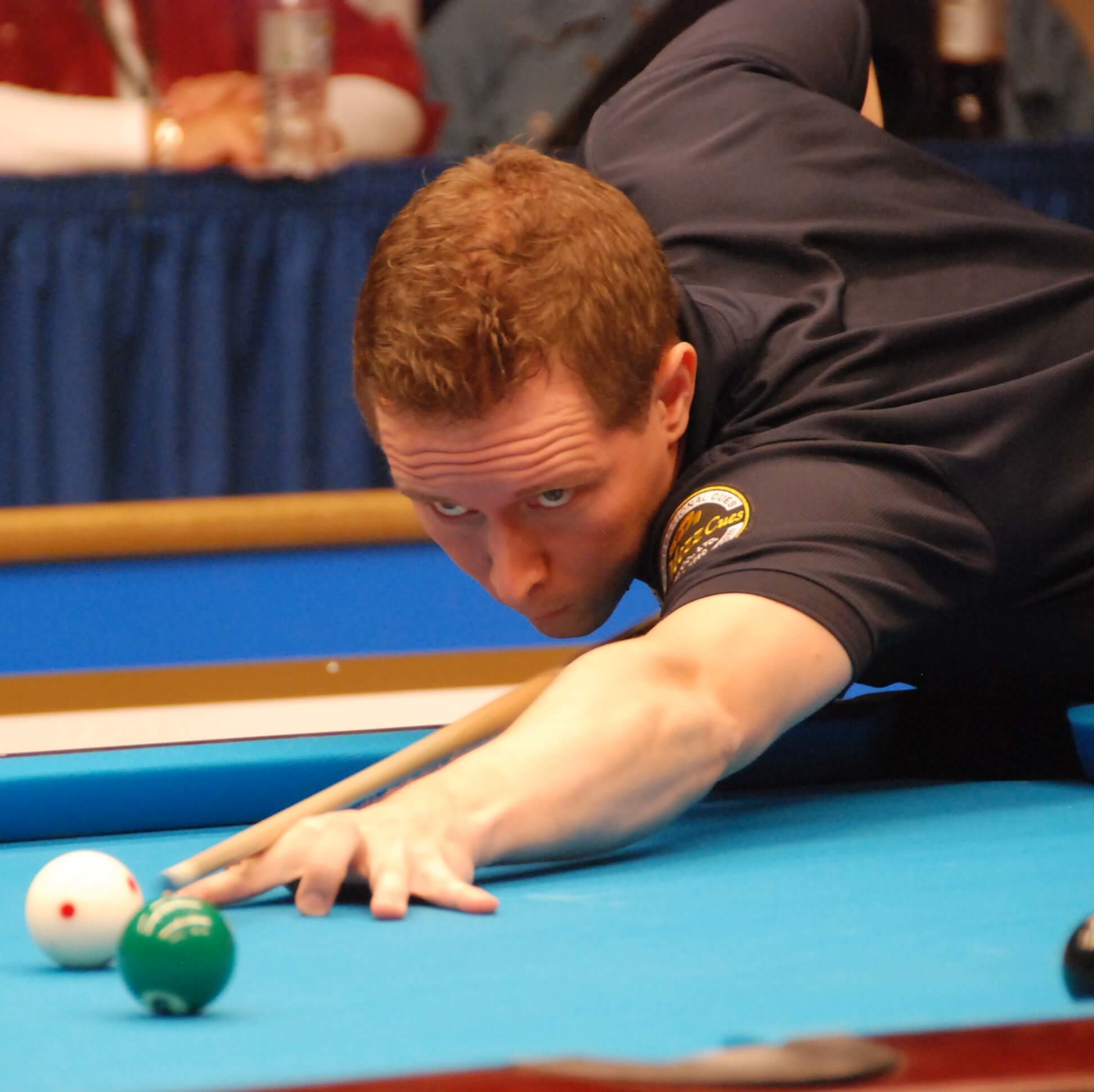
Eight-ball (also spelled 8-ball or eightball, and sometimes called solids and stripes, spots and stripes in the United Kingdom or highs and lows in Japan) is a pool (pocket billiards) game popular in much of the world, and the subject of international professional and amateur competition. Played on a pool table with six pockets, the game is so universally known in some countries that beginners are often unaware of other pool games and believe the word “pool” itself refers to eight-ball. The game has numerous variations, mostly regional. Standard eight-ball is the second most competitive professional pool game, after nine-ball, and for the last several decades ahead of straight pool. Unlike nine-ball, ten-ball, or seven-ball where the game’s name reflects the number of object balls used, eight-ball uses all fifteen object balls.
Eight Ball
History
The game of eight-ball is derived from an earlier game invented around 1900 (first recorded in 1908) in the United States and initially popularized under the name “B.B.C. Co. Pool” (a name that was still in use as late as 1925) by the Brunswick-Balke-Collender Company. This forerunner game was played with seven yellow and seven red balls, a black ball, and the cue ball. Today, numbered stripes and solids are preferred in most of the world, though the British-style offshoot, blackball, use the traditional colors (as did early televised “casino” tournaments in the United States). The game had relatively simple rules compared to today and was not added (under any name) to an official rule book (i.e., one published by a national or international sport governing body) until 1940.
Rules
- American-style eight-ball rules are played around the world by professionals and in many amateur leagues. Nevertheless, the rules for eight-ball may be the most contested of any billiard game. There are several competing sets of “official” rules. The non-profit World Pool-Billiard Association (WPA) – with national affiliates around the world, some of which long pre-date the WPA, such as the Billiard Congress of America (BCA) – promulgates standardized rules as Pool Billiards – The Rules of Play for amateur and professional play.Meanwhile, many amateur leagues – such as the American Poolplayers Association (APA) / Canadian Poolplayers Association (CPA), the Valley National Eight-ball Association (VNEA, international in scope despite its historic name) and the BCA Pool League (BCAPL) – use their own rulesets; most of these are at least loosely based on the WPA/BCA version. Millions of individuals play informally, using informal house rules which vary not only from area to area but even from venue to venue (“house rules“).
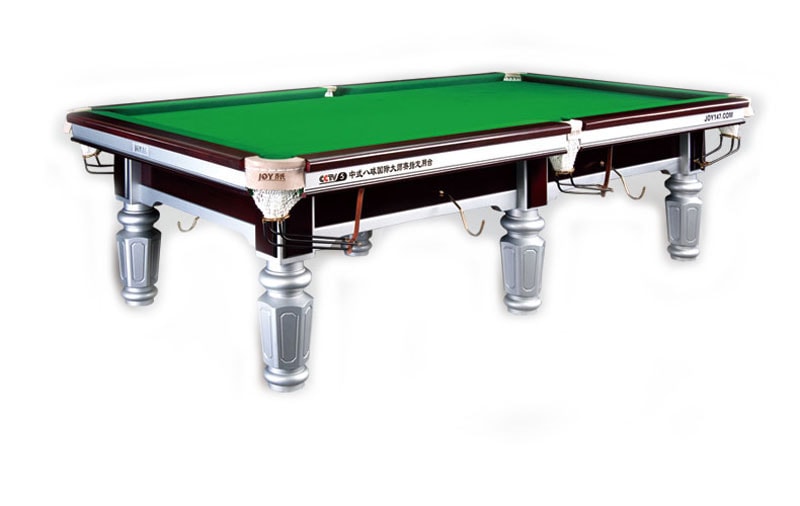


Equipments
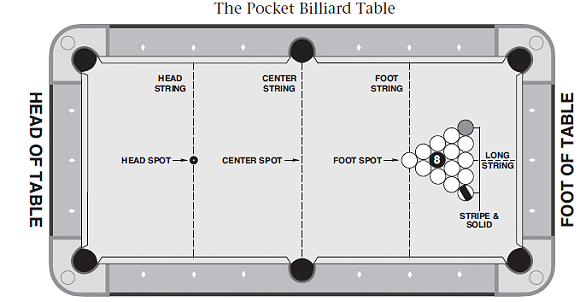
The regulation size of the table’s playing surface is 9 by 4.5 ft (2.7 by 1.4 m), though exact dimensions may vary slightly by manufacturer. Some leagues and tournaments using the World Standardized Rules may allow smaller sizes, down to 7 by 3.5 ft (2.1 by 1.1 m). Early 20th-century 10 by 5 ft (3.0 by 1.5 m) models are occasionally also still used. WPA professional competition generally employs regulation tables, while the amateur league championships of various leagues, including ACS, BCAPL, VNEA, and APA, use the 7-foot tables in order to fit more of them into the hosting venue.
There are seven solid-colored balls numbered 1 through 7, seven striped balls numbered 9 through 15, an 8 ball, and a cue ball. The balls are usually colored as follows:
- 1 and 9: yellow
- 2 and 10: blue
- 3 and 11: red
- 4 and 12: purple (TV: pink)
- 5 and 13: orange
- 6 and 14: green
- 7 and 15: maroon (TV: tan)
- 8: black
- Cue: white
Special sets designed to be more easily discernible on television substitute a rather light tan shade for the normally darker brown of the 7 and 15 balls, and pink for the dark purple of the 4 and 12; these alternative-color sets are now also available to consumers.
Association
The Valley National 8-Ball League Association (VNEA) is one of the world’s largest amateur pool (pocket billiards) leagues. As of 2010, there are nearly 100,000 individual members in some 1,400 weekly local leagues playing in over 10,000 pool halls, bars, and other venues in around 400 different cities, towns and suburbs in 36 U.S. states, and abroad.
The organization was founded in the United States in 1979 by equipment manufacturer Valley-Dynamo as the Valley 8-Ball League Association. It was later known as the Valley National 8-Ball Association, a name the league still uses sometimes (and as of 2012, the organization still retains the “VNEA” acronym in prose and in its logo). Despite its name, it is neither national, having leagues in eleven countries,[1]nor limited to the game of eight-ball, as team nine-ball, as well as an individual artistic pool and speed pool, are all now VNEA disciplines (some on a league basis, some only on a tournament basis). An annual, week-long VNEA International Pool Championships series (team, doubles and singles eight-ball, singles artistic pool) is held in Las Vegas, Nevada. The organization is headquartered in Bay City, Michigan. The president of VNEA’s board of directors is Michael Fowler (as of June 2010) and its executive director is R. Gregg Elliott (as of June 2010).